Determination of Pyridine, Quinoline and Styrene in Mainstream Tobacco Smoke
Health Canada
T-112 December 31, 1999
Table of Contents
- Scope of Applications
- Normative references
- Definitions
- Method Summary
- Apparatus and Equipment
- Reagents and Supplies
- Preparation of Glassware
- Preparation of Solutions
- Preparation of Standards
- Sampling
- Tobacco Product Preparation
- Smoking Machine Preparation
- Sample Generation
- Sample Analysis
- Quality Control
- Modifications for Intensive Smoking
- References
- Appendices
1 Scope of Applications
- Applicable to the isolation and quantitation of the pyridine, quinoline and styrene content of mainstream tobacco smoke by gas chromatograph/mass spectrometer (GC/MS).
2 Normative References
- Health Canada Method Test Method T-115 - Determination of Tar, Water, Nicotine and Carbon Monoxide in Mainstream Tobacco Smoke, 1999-12-31.
3 Definitions
- Refer to T-115 for definitions of terms used in this document.
4 Summary of Method
- Pyridine, styrene and quinoline are collected by passing the mainstream smoke of 20 cigarettes* through a 92 mm glass fiber filter disc (pad) and into cryogenic traps containing methanol. The pad is placed into an Erlenmeyer flask and the internal standard is added. The pad is extracted with the impinger solutions and the extracts are injected onto a GC/MS for quantitation.
*For other tobacco products, select a number such that breakthrough does not occur.
Note: The testing and evaluation of certain products against this test method may require the use of materials and or equipment that could potentially be hazardous and this document does not purport to address all the safety aspects associated with its use. Anyone using this test method has the responsibility to consult with the appropriate authorities and to establish health and safety practices in conjunction with any existing applicable regulatory requirements prior to its use.
5 Apparatus and Equipment
- Equipment needed to perform smoking analyses as specified in T-115.
- Equipment needed to perform conditioning of tobacco product as specified in T-115.
- Equipment needed to perform marking for butt length as specified in T-115.
- Analytical balance capable of measuring to at least four decimal places.
- 70 mL glass impingers with extra-coarse frits.
- Tygon tubing with connectors.
- Dewar flasks.
- Thermometer (-100 to 40 °C).
- 125 mL polymethylpentene (PMP) Erlenmeyer flasks with screw-caps or equivalent.
- 20 mL graduated cylinder.
- Wrist-action shaker.
- 10, 25, 50 and 100 mL volumetric flasks.
- Volumetric pipettes or gas-tight syringes for range 100 to 1000 µL.
- Autosampler vials with caps and Teflon-lined septa.
- Varian Saturn I GC/MS system consisting of an 8100 autosampler, a 3400 GC with a 1077 split/splitless injector and an ion trap detector (ITD) (or equivalent).
- Supelcowax 30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 µm column (or equivalent) with 1 m × 0.25 mm deactivated fused silica transfer line.
6 Reagents and Supplies
Note: All reagents shall be, at the least, recognized as analytical reagent grade in quality.
- Dry ice.
- Isopropanol (IPA).
- Methanol - Distilled-in-Glass.
- D5 - Pyridine - purity equal to or greater than 98 %.
- D7 - Quinoline - purity equal to or greater than 98 %.
- Pyridine.
- Quinoline.
- Styrene.
- Disposable 5 cc syringe.
- Syringe filters - 0.45 µm PTFE 25 mm (or equivalent).
7 Preparation of Glassware
- Glassware should be cleaned and dried in such a manner to ensure that contamination from glassware does not occur.
8 Preparation of Solutions
- Not applicable.
9 Preparation of Standards
- A primary stock solution of pyridine is prepared by accurately weighing approximately 100 mg of pyridine into a 10 mL volumetric flask. The flask is filled to the mark with methanol and mixed well. [Concentration: approximately 10 mg/mL].
- A primary stock solution of quinoline is prepared by accurately weighing approximately 100 mg of quinoline into a 100 mL volumetric flask. The flask is filled to the mark with methanol and mixed well. [Concentration: approximately 1 mg/mL].
- A primary stock solution of styrene is prepared by accurately weighing approximately 100 mg of styrene into a 10 mL volumetric flask. The flask is filled to the mark with methanol and mixed well. [Concentration: approximately 10 mg/mL].
- A mixed secondary stock solution is prepared by transferring 100 µL of each stock solution into a 50 mL volumetric flask, making to the mark with methanol and mixing well. [Concentration: approximately 20, 2 and 20 µg/mL, respectively].
- An internal standard stock solution of D5-pyridine is prepared by accurately weighing 100 mg of D5-pyridine into a 10 mL volumetric flask, filling the flask to the mark with methanol and mixing well.
- An internal standard stock solution of D7-quinoline is prepared by accurately weighing 25 mg of D7-quinoline into a 25 mL volumetric flask, filling the flask to the mark with methanol and mixing well.
- An internal standard (ISTD) spiking solution is prepared by diluting 2 mL of each of the ISTD stock solutions to 100 mL with methanol and mixing well. Aliquots of this spiking solution are stored in 25 mL vials with Teflon-lined caps and at minus 20 °C. [Concentration: approximately 200 and 20 µg/mL, respectively].
- Five calibration standard solutions are prepared by adding 100 µL ISTD spiking solution to each of five 10 mL volumetric flasks. The sides are rinsed with methanol, then appropriate aliquots (e.g. 2, 1, 0.5, 0.25 and 0.1 mL) of the secondary stock solution are added to each flask. The flasks are filled to the mark with methanol and mixed well.
- The solutions are transferred to a series of labeled autosampler vials, capped with Teflon-lined septa and stored at minus 20 °C until use. Note: Each vial is only used once.
10 Sampling
- The sampling of tobacco products for the purpose of testing shall be as specified in T-115.
11 Tobacco Product Preparation
- Product shall be conditioned as specified in T-115.
- Product shall be marked for butt length as specified in T-115.
- Cigarettes to be smoked under intense smoking conditions shall be prepared as specified in T-115.
12 Smoking Machine Preparation
- Ambient Conditions
- The ambient conditions for smoking shall be as those specified in T-115.
- Machine Conditions
- The machine conditions shall be as those specified in T-115 with the following modifications for a rotary machine as pictured in the following diagram.
The figure shows a graphical drawing of the apparatus set up for the sample generation and collection. Pneumatic pump is connected to the 20 port smoking machine and where the vapour phase is collected in impingers immersed in dry-ice/isopropanol slurry bath. The 92 mm cambridge filter pads are used to capture particulate phase.
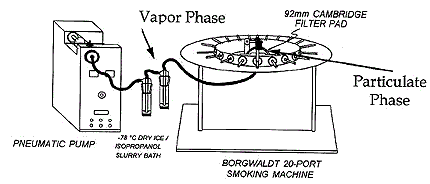
- Prepare the impingers by adding 20 mL of methanol into each impinger.
- Immerse the impingers into a dry-ice/IPA bath (temperature at or below -70 °C).
- Insert a pad holder with pad into the syringe of the smoking machine, and then hook up in series two impingers to the pad holder. Attach the first impinger to the large 92 mm filter holder.
- The machine conditions shall be as those specified in T-115 with the following modifications for a rotary machine as pictured in the following diagram.
13 Sample Generation
- TPM is collected as described in T-115.
14 Sample Analysis
- Extraction of filter pads
- Cut the 92 mm pad in quarters and place into a clean 125 mL PMP Erlenmeyer flask. Spike the pad with 400 µL of the ISTD solution.
- Transfer the contents of the first impinger into the flask. Rinse the first impinger with the contents of the second impinger and transfer the rinse into the flask.
- Close the flask and shake on the wrist-action shaker for 30 minutes.
- Pour 4 mL of the solution into a 5 mL syringe fitted with a syringe filter.
- Fill two labeled autosampler vials to the base of the neck and cap with an autosampler cap and Teflon-lined septum.
- Store samples at -20 °C for up to 48 hours prior to analysis.
- Instrument Analysis - GC/MS Conditions
- Injector temperature: 250 °C.
- Column temperature: 70 °C for two minutes.
3 °C per minute to 150 °C.
20 °C per minute to 250 °C, hold three minutes. - Column pressure: 12 psi or constant flow of 1.0 mL/minute
- Transfer line temperature: 240 °C.
- Manifold temperature: 240 °C.
- 1 µL of the methanol solution is injected at 5 µL per second onto the GC/MS, which is run in the splitless mode. (Split flow 20 mL/minute).
- The GC/MS is operated in full-scan mode (50 to 200 amu). The following ion peak areas are used for quantitation:
D5-pyridine 84
D7-quinoline 136
Pyridine 79
Quinoline 129
Styrene 104.
Note: The assignment of these masses is based on selection of the best response (i.e. the base peak) and the need to avoid possible contamination from interfering peaks which may contain similar ions.The choice of quantitation ions may be different for different instrument configurations.
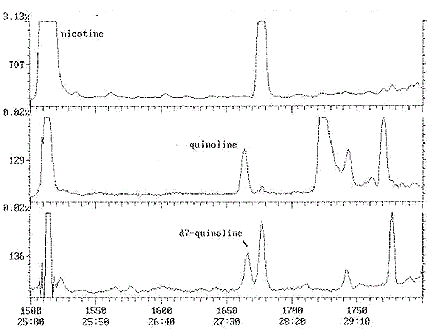
Note: Quantitation may be based on peak heights if interfering peaks cannot be completely resolved (see Appendices 1b and 1c).
- Calibration Curve
- A calibration curve is generated at the beginning of each sample set or "project". Each standard solution is injected once and a calibration file is built using the method for internal standard quantitation available with the Saturn quantitation software.
- A "check standard" is analyzed every 20 samples and at least once per run. This standard is treated as a sample and the observed value is compared to the expected value for that standard.
- If the results are within 10 % of expected, the calibration is still valid.
- If the results differ by more than 10 % of expected, the calibration is no longer valid and a new calibration curve must be generated.
- Sample Calculation
- The software on the GC/MS is used to generate results for each analyte based on the concentrations of the standard solutions. The results are reported in µg/mL. To calculate the final results, the following calculation is used:
Analyte (µg/cigarette) = [Conc. of Analyte in Sample (µg/mL) × Volume (mL)] / # of cigarettes
- The software on the GC/MS is used to generate results for each analyte based on the concentrations of the standard solutions. The results are reported in µg/mL. To calculate the final results, the following calculation is used:
15 Quality Control
- Typical Chromatograms
- See Appendices.
- Recoveries and Levels of Contamination
- This involves the use of laboratory reagent blanks (LRB) to evaluate potential interference of the reagents. One LRB should be analysed every 20 samples. LRB preparation: A 92 mm pad is quartered and placed in a PMP Erlenmeyer with 400 µL of the ISTD solution and 40 mL of methanol. The LRB is then treated as a sample through the rest of the procedure. Typical results are non-detected (ND) for all analytes.
Note: In lieu of an LRB, a smoking blank can be used to monitor contamination of reagents and the air in the smoking room. This involves conducting a smoking run with the same number of puffs as a control cigarette but with no cigarette in place. Typical result for a smoking room blank is between 0.06 and 0.12 µg/mL (equivalent to 0.12 and 0.24 µg/cigarette) for pyridine and styrene and ND for quinoline. - A laboratory fortified blank (LFB) may be analyzed to evaluate the extent of potential analyte loss. A 92 mm pad is quartered and placed in a flask with 400 µL of the ISTD solution, an appropriate aliquot of the secondary mixed stock solution and 40 mL of methanol. The LFB is then treated as a sample through the rest of the procedure. The recoveries should be close to 100 %.
- A laboratory fortified matrix (LFM) may be analysed to assess potential matrix interference. LFM preparation: A sample of a control brand is smoked and the pad transferred to the flask. The pad is spiked with the ISTD solution and an aliquot of the mixed secondary stock solution. The impinger solutions are added to the pad and the sample is taken through the remainder of the procedure. The recoveries should be close to 100 %.
- This involves the use of laboratory reagent blanks (LRB) to evaluate potential interference of the reagents. One LRB should be analysed every 20 samples. LRB preparation: A 92 mm pad is quartered and placed in a PMP Erlenmeyer with 400 µL of the ISTD solution and 40 mL of methanol. The LRB is then treated as a sample through the rest of the procedure. Typical results are non-detected (ND) for all analytes.
- Method Detection Limit (MDL)/Limit of Quantitation (LOQ)
The MDL can be defined as the level which gives a signal to noise ratio of three to one. The LOQ can be defined as the level which gives a signal to noise ratio of 10 to one. MDLs should be determined for each system and may differ from instrument to instrument.
Note: Because this method involves the analysis of the methanol soluble components of whole tobacco smoke, with no sample clean-up, the chromatography must be very carefully monitored so that the peaks are sharp and the analytes of interest are well resolved from other components. - Stability of Reagents and Samples
- Stock solutions are stable for at least six months if stored at -20 °C.
- Calibration standards are stable for at least one week if stored at -20 °C.
- Once punctured, the more volatile pyridine may be lost so vials are typically used once and discarded.
- Samples are stable in the freezer for at least one week if the septum has not been punctured. It is essential that at least two vials be prepared for each sample as the vial is discarded once punctured.
16 Modifications for Intense Smoking Conditions
- Under intense smoking conditions, 10 cigarettes are smoked instead of 20.
17 Reference
- White, E., Uhrig, M., Johnson, T., Gordon, B., Hicks, R., Borgerding, M., Coleman, W., and Elder, J. Quantitative Determination of Selected Compounds in a Kentucky 1R4F Reference Cigarette Smoke by Multidimensional Gas Chromatography and Selected Ion Monitoring - Mass Spectrometry, Journal of Chromatographic Science, 26, 1990, p. 393-399.
Appendices
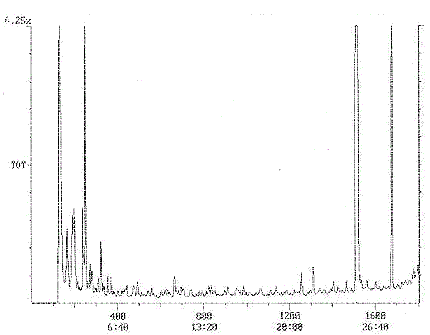
Appendix 1a: Typical Chromatogram
Chromatogram Plot
Comment : SUPELCOWAX 30X0. 25X0. 25 1ZPSI 70CSTART INJ250C FASTINJ (5)
Scan No : 1000
Retention time : 30:00
Mass Range : 50 - 200
Plotted : 1 to 1000
Range : 1 to 1800
Appendix 1b: Typical Chromatogram - Pyridine
Chromatogram Plot
Comment : SUPELCOWAX 30X0. 25X0. 25 1ZPSI 70CSTART INJ250C FASTINJ (5)
Scan No : 400
Retention time : 6:40
Mass Range : 50 - 200
Plotted : 100 to 400
Range : 1 to 1800
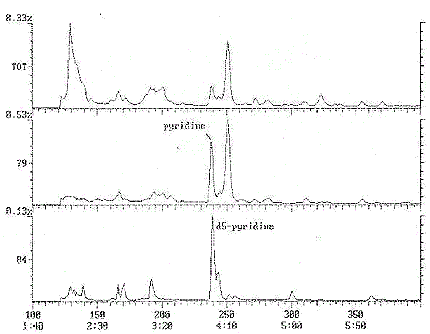
Appendix 1c: Typical Chromatogram - Quinoline
Chromatogram Plot
Comment : SUPELCOWAX 30X0. 25X0. 25 1ZPSI 70CSTART INJ250C FASTINJ (5)
Scan No : 1800
Retention time : 30:00
Mass Range : 50 - 200
Plotted : 1500 to 1800
Range : 1 to 1800
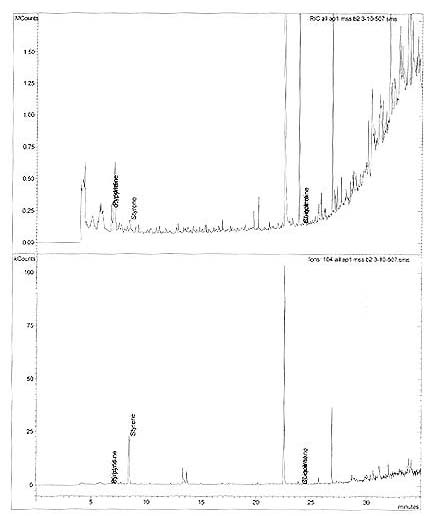
Appendix 1D: Typical Chromatogram - Styrene
Sample: AP1 MSS B2 3-10-507
Sample Notes:
Operator:
Scan Range: 1 - 2099
Time Range: 0.00 - 34.97