Determination of Ammonia in Whole Tobacco
Health Canada
T-302 December 31, 1999
Table of Contents
- Scope of Applications
- Normative References
- Method Summary
- Apparatus and Equipment
- Reagents and Supplies
- Preparation of Glassware
- Preparation of Solutions
- Preparation of Standards
- Sampling
- Sample Analysis
- Quality Control
- References
- Appendix
1 Scope of Applications
- Applicable to the isolation and quantitation of ammonia in whole tobacco by High Performance Liquid Chromatograpy (HPLC).
2 Normative References
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) D1193-77 - Standard Specifications for Reagent Water, Version 1977.
- Health Canada Test Method T-115 - Determination of Tar, Water, Nicotine and Carbon Monoxide in Mainstream Tobacco Smoke, 1999-12-31.
3 Method Summary
- Approximately 3 g of whole tobacco is placed into a pre-weighed scintillation vial and lyophilized for 48 hours. After the moisture content is determined, the sample is then ground using the # 40 (40 sections / square inch) screen on a bench top grinder.
- One hundred mg of freeze dried tobacco is accurately weighed into a 16 mL culture tube with cap. The sample is extracted into 10 mL of 0.025N H2SO4 (25 mN) on a wrist action shaker for 30 minutes. This mixture is then filtered through a 0.45 µm syringe filter into a 7 mL scintillation vial for storage from which an aliquot is taken for analysis by cation exchange chromatography.
Note: Dependent on the amount of sample available, the amount of sample used for analysis may be modified as long as the sample appears homogeneous and the ratio of sample weight to extraction solution remains the same (i.e. 0.1g to 10 mL solution; 1:100). - A 35 µL volume of sample is injected onto an cation exchange analytical column that uses a Carboxylic acid/Phosphonic acid functional group to achieve separation of ammonium and monovalent cations. In order to adequately resolve sodium from the ammonium cation for quantitation, a 0.003 N (3 mN) sulfonic acid solution is used as the mobile phase. After the ammonium ion has eluted, a gradient using 0.2 N (200 mN) H2SO4 to a 0.05 N (50 mN) H2SO4 concentration is used to remove any divalent cations and quaternary amines that may be present in the sample and may interfere with subsequent samples.
- Detection of cations is achieved using a suppressed conductivity detector in external water mode (CSRS-II). This method of detection reduces background conductivity from the mobile phase, thus increasing the sensitivity of the detector for the analyte.
- Quantitation is obtained from a five point external standard calibration using the peak height response of ammonium sulphate. The amount of ammonia (in µg/g of whole tobacco) is determined by calculating the amount of ammonia present in the analytical solution, then multiplying by the appropriate multiplier (10 mL) and divisor (g of whole tobacco). Results from this calculation are expressed on a "Dry Matter" basis.
Note: The testing and evaluation of certain products against this test method may require the use of materials and or equipment that could potentially be hazardous and this document does not purport to address all the safety aspects associated with its use. Anyone using this test method has the responsibility to consult with the appropriate authorities and to establish health and safety practices in conjunction with any existing applicable regulatory requirements prior to its use.
4 Apparatus and Equipment
- Lyophilizer.
- Wrist action shaker.
- Analytical balance measuring to at least four decimal places.
- Bench top grinder with # 40 (40 sections /square inch) screen.
- Glass Fibre Syringe filter (25 mm × 0.45 µm).
- 25, 50, and 100 mL volumetric flasks.
- Disposable 5 cc syringe.
- 7 mL screw top vials with aluminum lined cap.
- Septa, 8 mm, Blue TFE/SIL, 60 MIL.
- 2 mL auto sampler vials and caps.
- High Performance Liquid Chromatograph (HPLC) consisting of:
- Refrigerated autosampler with 100 µL partial fill loop.
- Tertiary gradient system.
- Column heater.
- Dionex ED-40 conductivity detector or equivalent.
- Dionex CTC-1 cation trap or equivalent.
- Dionex CSRS-II conductivity suppresser in external water mode or equivalent.
- Data collection system.
- Dionex IonPac CS12A cation exchange analytical column (250 mm × 4 mm) or equivalent.
- Dionex IonPac CG12A cation exchange guard column or equivalent.
- 125 ml Polymethylpentene (PMP) Erlenmeyer flasks with screw top caps and/or 16 mL culture tubes with High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) screw top caps (dependent on extraction weights and volumes used).
5 Reagents and Supplies
Note: All reagents shall be, at the least, recognized as analytical reagent grade in quality.
- Ammonium Sulphate > 99 % purity.
- Sulphuric Acid > 96 % purity.
- Methanesulphonic Acid (MSA) - 100 %.
- Type I water (as per ASTM D1193).
6 Preparation of Glassware
- Glassware should be cleaned and dried in such a manner to ensure that contamination from glassware does not occur.
- Immediately prior to use, all extraction tubes are washed with 0.1N H2SO4, rinsed three times with deionized water, and three times with Type I water.
7 Preparation of Solutions
- Sulphuric Acid, 0.10N - Stock Standards Solution
- Carefully add 5.108 g of H2SO4 (96% w/w) to 900 mL of Type I water.
- Mix and dilute to 1 L with Type I water.
- Sulphuric Acid, 0.025N - Extraction Solution
- Carefully add 1.277 g of H2SO4 (96% w/w) to 900 mL of Type I water.
- Mix and dilute to 1 L with Type I water.
- Sulphuric Acid, 0.20N - Solution C (Ion Chromatography)
- Carefully add 10.216 g of H2SO4 (96% w/w) to 900 mL of Type I water.
- Mix and dilute to 1 L with Type I water.
- MSA 3mN - Solution A (Ion Chromatography)
- Carefully add 0.2883 g of Methanesulphonic Acid (MSA) to 900 mL of Type I water.
- Mix and dilute to 1 L with Type I water.
8 Preparation of Standards
- Primary (1°) Ammonium Stock:
- Accurately weigh 0.20 g of ammonium sulphate into a 50 mL volumetric flask.
- Dissolve in 0.10N H2SO4.
- Make up to volume.
- Prepare fresh every 10 working days.
Note: This corresponds to a 1.0898 mg/mL NH4+ ion stock solution - Working Standards: The following table demonstrates the working standards for 7 samples, including the volume of the primary ammonia standard, the final volume and concentration of the working stock standards.
Working Standards: Standard
#Volume of 1o
Standard
(µL)Final Volume
(mL)Concentration
[µg/mL]0 0 25 0.000 1 250 25 10.898 2 175 25 7.6283 3 75 25 3.2693 4 75 50 1.6346 5 50 100 0.5449 6 20 100 0.2180
Note: All run standards are made to volume to have a 0.025 N (25 mN) H2SO4 concentration. Prepare fresh every five working days.
Note: All weights, volumes, and purity must be recorded and used to accurately calculate the standard concentrations.
9 Sampling
- The sampling of tobacco products for the purpose of testing shall be as specified in T-115.
10 Sample Analysis
- Sample Preparation
- Freeze-dry the whole tobacco in a lyophilizer for 48 hrs.
- Mill the whole tobacco in a bench top grinder to a 40 mesh size.
- Weigh accurately 100 mg of ground tobacco into a 16 mL culture tube.
- Add 10 mL of extraction solution and shake for 60 minutes on a wrist action shaker.
- Allow mixture to settle (approximately one hour) and filter the solution through a syringe filter into an 8 mL storage vial noting to rinse the vial initially with approximately 1 mL of sample.
- 250 µL of the filtrate is pipetted directly into a 2 mL autosampler vial where 1000 µL of extraction solution is added (1:5 dilution).
Note: This dilution represents the standard dilution required for most flue-cured tobacco products. The filtrate of other tobacco products may required different dilutions (or none at all) to fall within the calibration range. All dilutions are made with the extraction solution.
Note: Dilutions are not required to be performed in this manner. Dilutions using volumetric flasks may be more accurate (but more time consuming and susceptible to contamination).
- Ion Chromatography Analysis
- Dionex ED-40 Conditions
Suppressor Conductivity (SRS): 100 mA.
Scale: 20 uS.
Output: Offset.
Offset: 1% of Full Scale. - Autosampler : Injection Volume
- Analyze using a 100 µL partial fill sample loop with the parameter for injection volume in the sample list at 35 µL with a 60 µL wash to flush the sample loop.
- Column Temperature: 30 °C.
- Mobile Phase / Gradient Conditions (Tertiary Gradient System)
Solvent A: 0.003 N MSA.
Solvent B: Type I water.
Solvent C: 0.2N H2SO4.
Flow: 1.5 mL/minute .
Gradient: Minor adjustments may be required depending on column conditions and resolution of analyte.
The following table shows the ion chromatography analysis and mobile phase composition and tertiary gradient conditions during a 25 min run. The equilibration time is at 9 minutes. The flow is 1.5 mL/minute.
Time (minute) Composition % A % B % C 0.00 100 0 0 13.00 100 0 0 13.01 0 80 20 14.00 0 80 20 14.01 0 90 10 19.00 0 90 10 19.01 0 99 1 20.00 0 99 1 25.00 99 1 0 25.00 Method End Action: Equilibrate Equilibration Time: 9.00 minutes
- Dionex ED-40 Conditions
- Calculations
- Determination of Response Factor (RF)
- An initial calibration is performed by running prepared standards from high concentration to low concentration (injecting the very first standard a minimum of two times until the response and retention time are constant).
- A calibration curve is prepared by plotting the concentration of NH4+ ion in the standard vs. the peak height response from the conductivity detector.
- The RF is the slope of the line as determined by linear regression (Height counts / unit concentration).
- Determination of Ammonium Ion
NH4+ [µg/g] = [peak height × volume extractant (mL) × final volume (mL)] / [RF × weight used (g) × aliquot volume (mL)]
where the aliquot volume (mL) is the volume transferred to the autosampler vial.
Note: Results are calculated on a "Dry Matter Basis" since a dried sample is used for the weight. - Determination of Ammonia
NH3 [µg/g] = NH4+ [µg/g] × 17/18.
where 17/18 corrects for molecular weight.
- Determination of Response Factor (RF)
11 Quality Control
- Typical Chromatogram
- See Appendix 1.
- Typical Control Parameters
- Before processing any samples, the analyst should demonstrate, through the analysis of a reagent water blank, that interferences from the analytical system, glassware, and reagents are not present.
- The blank samples should be carried through all stages of the sample preparation and measurement steps.
- For each analytical batch, a laboratory reagent blank (LRB) and laboratory fortified matrix (LFM) must be analyzed. The blank and spiked samples must be carried through all stages of the sample preparation and measurement steps.
- As a control measure, a tobacco with a known ammonia content should accompany each set of shaking on the wrist action shaker.
- Recoveries and Levels of Contamination
- Typical recoveries of Laboratory Fortified Blanks (LFB) and Laboratory Fortified Matrix (LFM) samples range from 85 - 110 % when a spiked solution (or sample) is carried out through the entire extraction process.
- Typical Laboratory Reagent Blanks (LRB) have a value of 0 µg/g. Contamination (> 0 µg/g) of this type is usually associated with contamination of the filter pad during conditioning or an inadequate cleaning of glassware.
- Method Detection Limits (MDL) / Limit of Quantitation (LOQ)
- The method detection limit (MDL) is determined by analyzing the lowest standard level a minimum of 10 times as an unknown over several days. The MDL is calculated as three times the standard deviation of these determinations.
- The MDL (on a ng/g basis) can be modified by varying the amount of tobacco used and the volumes used for extraction and clean up in the procedure.
- The practical limit of quantitation (LOQ) is determined by analyzing the lowest standard level a minimum 10 times as an unknown over several days. The LOQ is calculated as 10 times the standard deviation of these determinations.
- For true samples, the MDL/LOQ is dependent on the resolution and the amount of sodium ion present in the sample, since the tail of a huge sodium peak may mask any ammonium ion present.
- Stability of Reagents and Samples
- Primary standards should be prepared fresh every 10 working days and stored at 4 °C.
- Run standards should be prepared fresh from the stock solution weekly and stored at 4 °C.
- Samples are stable for 48 hours at 4 °C.
12 References
- Risner, C.H., Conner, J.M. Collection of Ammonia in Indoor Air by Means of a Weak Cation Exchange Cartridge. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, Vol. 10, p. 1417-1423, 1991.
- Nanni, E.J., Lovette, M.e., Hicks, R.D., Fowler, K.W. and Borgerding, M.F. Separation and Quantitation of Monovalent and Cationic Species in mainstream Cigarette Smoke Aerosols by High- Performance Ion Chromatography. Journal of Chromatographic Science, Vol. 28, August 1990.
- IonPac CS12A Analytical Column, Installation Instructions and Troubleshooting Guide, Document No. 031132, Revision 01, Dionex Corporation, 1995.
13 Appendix
Appendix: Typical Chromatogram
This figure demonstrates a typical chromatogram for the overlay of a standard and tobacco of a reference cigarette with a 5% offset.
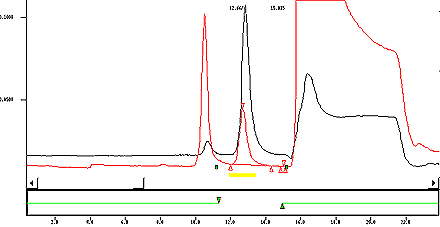
An overlay of a standard and tobacco of a reference cigarette with a 5 % offset.